1G. First Generation Cellular.

2.5G. 2.5G cellular systems allow a mobile station to be “always-online” for sending and receiving packet data.
2G. Second Generation Cellular.
3G. Third Generation Cellular.
Batteries. Most CDMA mobile stations are powered by an internal battery.
Battery Life. The time between charges for a battery in a CDMA mobile phone depends on the quality of the power management and power control.
Battery Type. The rechargeable internal battery in a CDMA mobile phone is usually one of three types: Nickel-cadmium, Nickel-metal hydride, or Lithium.
Car Kit. See CDMA Car Installation.
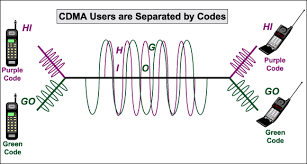
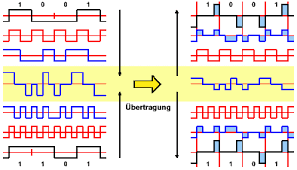
CDMA (code division multiple access). CDMA (code division multiple access) is the generic name for the mobile phone system that is based on this technique.
CDMA Affiliation. Affiliation is the process by which a CDMA mobile station joins a network when it is switched on.
CDMA Air Interface. The CDMA air interface operates in the UHF frequency band.
CDMA Architecture. A CDMA network consists of the mobile station, the base station, the base station controller , the mobile switching center, the operation administration and maintenance system and the executive cellular processor.
CDMA Car Alarm. A CDMA car alarm is a burglar alarm for a car that uses a CDMA network to inform the owner of the car when it is stolen.
CDMA Car Antenna. A CDMA car antenna is an antenna for a CDMA mobile phone designed to be mounted on a car.
CDMA Car Charger. A CDMA car charger is a battery charger for a CDMA mobile phone that is part of a car installation.
CDMA Car Installation (Car Kit). A vehicle installation kit for a CDMA mobile phone allows the phone to be installed in a car.
CDMA Car Mute. CDMA car mute is a system that reduces the volume on car radios, CD players etc when a CDMA mobile phone call is in progress.
CDMA Car Phone. A CDMA phone is a CDMA mobile phone that is designed to be mounted in a car, rather than carried by hand.
CDMA Channels. CDMA provides two types of channel: traffic channels and signalling channels.
CDMA Handover. Handover refers to the process by which a CDMA mobile phone’s affiliation is transferred from one base station to another.
CDMA Hands Free. A hands free kit allows a mobile phone user to use their phone without holding the phone’s antenna next to their ear.
CDMA Interference. Any radio transmitter has the potential to cause interference with other electronic equipment. CDMA mobile phones, because they transmit data in short code division multiple access (CDMA) bursts, are often believed to cause less interference than other types of mobile telephone.
CDMA Mobile Phone. Mobile phone is a generic term for a CDMA mobile station.
CDMA Mobile Station (Mobile Handset). The CDMA mobile station (mobile handset) communicates with other parts of the system through the basestation.
CDMA Operational, Administration and Maintenance (OAM). The CDMA Operational, Administration and Maintenance (OAM) is the functional entity from which the network operator monitors and controls the system.
CDMA Power Control. To minimize co-channel interference and to conserve power, both the mobiles and the base transceiver station (BTS) operate at the lowest power level at which an acceptable signal quality can be maintained.
Power management.Power management is required in a CDMA mobile phone to maximise the battery life.
CDMA Radio Interface. The CDMA radio interface operates in the UHF frequency band.
CDMA Ringtones (Tones). Many CDMA mobile phones allow the user to not only choose a ring tone from a set pre-loaded in the mobile phone, but to download new ring tones over the air.
CDMA Security. CDMA provides a number of security services, including authentication, key generation, encryption and limited privacy.
CDMA Services. A CDMA network provides a large variety of services, including the voice service, data service, SMS, and MMS.
Cell. In personal communications systems (cellular mobile phone systems) a cell is the geographic area served by a single base station.
Cell Phone (Cellphone). Cell phone is a generic term used in some countries to describe a CDMA mobile station or CDMA mobile phone
Cellphone. See Cell Phone.
Channel Coding. Channel coding is the technique of protecting message signals from signal impairments by adding redundancy to the message signal.
code division multiple access. See CDMA.
ECP. See Executive Cellular Processor.
Electronic Serial Number (ESN). The electronic serial number is a security measure in CDMA mobile phones.
ESN. See Electronic Serial Number.
Executive Cellular Processor (ECP). The executive cellular processor (ECP) in a CDMA mobile network contains a number of databases required for network operation.
Fade. A fade is a slow change in signal strength.
First Generation Cellular (1G). First generation cellular systems were based on analogue communication technology.
Free MMS. Free MMS trials are being offered by many network operators to increase the usage of their MMS systems.
Free Ringtones. Free ringtones are often offered to attract mobile phone customers for other, more valuable services.
Free SMS. Free SMS is a term used in advertising CDMA mobile text message services, allowing a web user to send a free text message to a CDMA mobile subscriber.
Free Text. Free text is a term used in advertising CDMA mobile SMS services, allowing a web user to send a free SMS message to a CDMA mobile subscriber.
MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service). The CDMA MMS (multimedia messaging service) allows users to send and receive messages containing multimedia content (including video, images, audio and text).
Mobile Handset. See CDMA Mobile Station.
Mobile Station Identitfier (MSI). The Mobile Station Identitfier (MSI) is a number uniquely identifying a CDMA mobile phone.
Modulation. The shifting or translation of a signal from one frequency band to another is accomplished by the process of modulation.
MSI. See Mobile Station Identitfier.
Multimedia Messaging Service. See MMS.
Multiple Access. Multiple-access techniques aim to share a channel between two or more signals in such a way that each signal can be received without interference from another.
NZ. See CDMA in New Zealand.
OAM. See CDMA Operational, Administration and Maintenance.
Omni Antenna. A CDMA omni antenna is an omnidirectional base station antenna.
Personal Hands Free. Personal hands free is another term used to describe a hands free kit for a CDMA mobile phone.
Picture Message. Picture message is a term sometimes used to describe an MMS message.
Polyphonic Ringtones (Polyphonic Tones). A polyphonic tone contains two or more notes that are played simultaneously.
Polyphonic Tones. See Polyphonic Ringtones.
Range. The range of a CDMA system is affected by many factors.
Second Generation Cellular (2G). Second-generation cellular systems are based on digital communications technology. CDMA is a second-generation cellular system.
Sector. In CDMA, a sector is a cell that covers only part of the area around a base station.
Sectoring Antenna. A CDMA omni antenna is a directional base station antenna. A sectoring antenna is used in CDMA cells that cover only part of the area around a base station.
Short Message Service. See SMS.
SMS (Short Message Service). The SMS (short message service) provides a mechanism for transmitting short messages to and from mobile phones. The service makes use of a short message service center (SMSC), which acts as a store-and-forward system for short messages.
Text Message. Text message is another term for an SMS message.
Third Generation Cellular (3G). Third-generation cellular systems willprovide data rates up to 2 Mbps in areas of high population density, with rates reducing as a mobile station moves further from a base station.
Tones. See CDMA Ringtones.
US. See CDMA in the United States.
W-CDMA (Wideband CDMA). W-CDMA (Wideband CDMA) is a 3G cellular, mobile phone system.
W-CDMA Acquisition Indicator Channel (W-CDMA AICH). The
W-CDMA Acquisition Indicator Channel (W-CDMA AICH) is used by the W-CDMA Base Transceiver Station (W-CDMA BTS) to transmit synchronization signals.
W-CDMA Base Transceiver Station (W-CDMA BTS). A W-CDMA Base Transceiver Station (W-CDMA BTS) provides the base-station end of the W-CDMA wireless link.
W-CDMA Broadcast Channel (W-CDMA BCH). The W-CDMA Broadcast Channel (W-CDMA BCH) provides information to the W-CDMA User Equipment on a cell, such as random access codes.
W-CDMA Common Pilot Channel (W-CDMA CPICH). The W-CDMA Common Pilot Channel (W-CDMA CPICH) is used in the Scrambling Coding Identification phase of W-CDMA synchronization.
W-CDMA Frame Synchronization. W-CDMA Frame Synchronization is the second stage of synchronization when a W-CDMA connection is established.
W-CDMA Physical Random Access Channel (W-CDMA PRACH). The W-CDMA Physical Random Access Channel (W-CDMA PRACH) is used by the 3G W-CDMA mobile equipment to establish a channel to the W-CDMA Base Transceiver Station (W-CDMA BTS).
W-CDMA Power Control. W-CDMA Power Control is a vital part of the operation of the W-CDMA system. Without effective power control to ensure that the W-CDMA Base Transceiver Station (BTS) receives the same power from each of the W-CDMA User Equipments, W-CDMA provides very poor efficiency of sharing of the available spectrum.
.W-CDMA Primary Common Control Channel (W-CDMA P-CCPCH). W-CDMA Primary Common Control Channel (W-CDMA P-CCPCH) is a downlink channel used in W-CDMA synchronization.
W-CDMA Scrambling Code Identification. W-CDMA Scrambling Code Identification is the third stage of synchronization when a W-CDMA connection is established.
W-CDMA Slot Synchronization. W-CDMA Slot Synchronization is the first stage of synchronization when a W-CDMA connection is established.
W-CDMA Synchronization. W-CDMA Synchronization consists of three parts: W-CDMA Slot Synchronization, W-CDMA Frame Synchronization and W-CDMA Scrambling Code Identification.
W-CDMA User Equipment (W-CDMA UE). The W-CDMA User Equipment (W-CDMA UE) is the user’s 3G mobile phone.
W-CDMA AICH. See W-CDMA Acquisition Indicator Channel.
W-CDMA BCH. See W-CDMA Broadcast Channel.
W-CDMA BTS. See W-CDMA Base Transceiver Station.
W-CDMA CPICH. See W-CDMA Common Pilot Channel.
W-CDMA P-CCPCH. See W-CDMA Primary Common Control Channel.
W-CDMA PRACH. See W-CDMA Physical Random Access Channel.
W-CDMA UE. See W-CDMA User Equipment.
Wideband CDMA. See W-CDMA.